
The matplotlib.text.Text instances have a variety of properties which can be configured via keyword arguments to the text commands (e.g., title(), xlabel() and text()).
| Property | Value Type |
|---|---|
| alpha | float |
| backgroundcolor | any matplotlib color |
| bbox | rectangle prop dict plus key 'pad' which is a pad in points |
| clip_box | a matplotlib.transform.Bbox instance |
| clip_on | [True | False] |
| clip_path | a Path instance and a Transform instance, a Patch |
| color | any matplotlib color |
| family | [ 'serif' | 'sans-serif' | 'cursive' | 'fantasy' | 'monospace' ] |
| fontproperties | a matplotlib.font_manager.FontProperties instance |
| horizontalalignment or ha | [ 'center' | 'right' | 'left' ] |
| label | any string |
| linespacing | float |
| multialignment | ['left' | 'right' | 'center' ] |
| name or fontname | string e.g., ['Sans' | 'Courier' | 'Helvetica' ...] |
| picker | [None|float|boolean|callable] |
| position | (x,y) |
| rotation | [ angle in degrees 'vertical' | 'horizontal' |
| size or fontsize | [ size in points | relative size, e.g., 'smaller', 'x-large' ] |
| style or fontstyle | [ 'normal' | 'italic' | 'oblique'] |
| text | string or anything printable with ‘%s’ conversion |
| transform | a matplotlib.transform transformation instance |
| variant | [ 'normal' | 'small-caps' ] |
| verticalalignment or va | [ 'center' | 'top' | 'bottom' | 'baseline' ] |
| visible | [True | False] |
| weight or fontweight | [ 'normal' | 'bold' | 'heavy' | 'light' | 'ultrabold' | 'ultralight'] |
| x | float |
| y | float |
| zorder | any number |
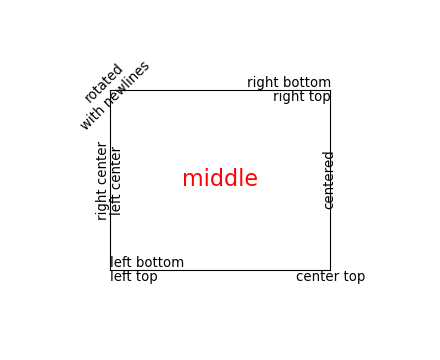
You can layout text with the alignment arguments horizontalalignment, verticalalignment, and multialignment. horizontalalignment controls whether the x positional argument for the text indicates the left, center or right side of the text bounding box. verticalalignment controls whether the y positional argument for the text indicates the bottom, center or top side of the text bounding box. multialignment, for newline separated strings only, controls whether the different lines are left, center or right justified. Here is an example which uses the text() command to show the various alignment possibilities. The use of transform=ax.transAxes throughout the code indicates that the coordinates are given relative to the axes bounding box, with 0,0 being the lower left of the axes and 1,1 the upper right.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as patches
# build a rectangle in axes coords
left, width = .25, .5
bottom, height = .25, .5
right = left + width
top = bottom + height
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([0,0,1,1])
# axes coordinates are 0,0 is bottom left and 1,1 is upper right
p = patches.Rectangle(
(left, bottom), width, height,
fill=False, transform=ax.transAxes, clip_on=False
)
ax.add_patch(p)
ax.text(left, bottom, 'left top',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, bottom, 'left bottom',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='bottom',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, top, 'right bottom',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='bottom',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, top, 'right top',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, bottom, 'center top',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='top',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'right center',
horizontalalignment='right',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'left center',
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(0.5*(left+right), 0.5*(bottom+top), 'middle',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
fontsize=20, color='red',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(right, 0.5*(bottom+top), 'centered',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation='vertical',
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.text(left, top, 'rotated\nwith newlines',
horizontalalignment='center',
verticalalignment='center',
rotation=45,
transform=ax.transAxes)
ax.set_axis_off()
plt.show()
(Source code, png)