
(png)
(png)
(png)
(png)
(png)
(png)
(png)
#!/usr/bin/python
#
# Example boxplot code
#
from pylab import *
# fake up some data
spread = rand(50) * 100
center = ones(25) * 50
flier_high = rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = rand(10) * -100
data = concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low), 0)
# basic plot
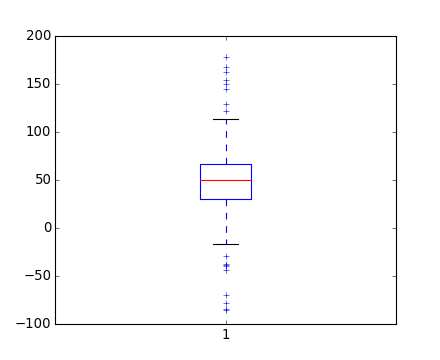
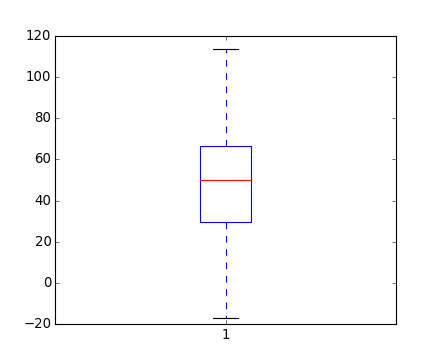
boxplot(data)
# notched plot
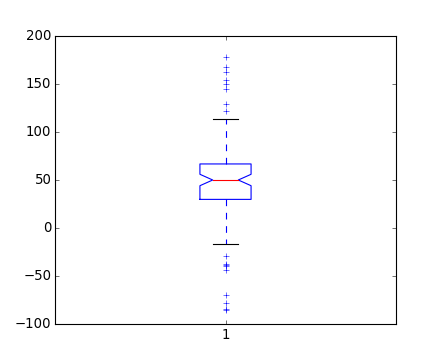
figure()
boxplot(data, 1)
# change outlier point symbols
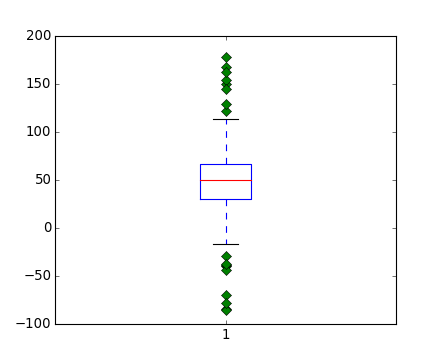
figure()
boxplot(data, 0, 'gD')
# don't show outlier points
figure()
boxplot(data, 0, '')
# horizontal boxes
figure()
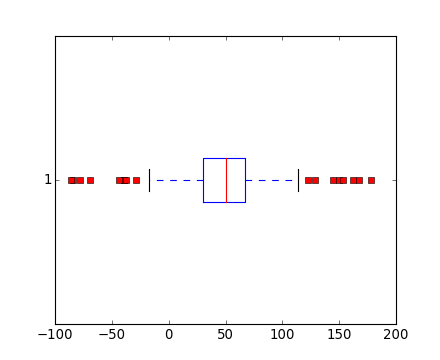
boxplot(data, 0, 'rs', 0)
# change whisker length
figure()
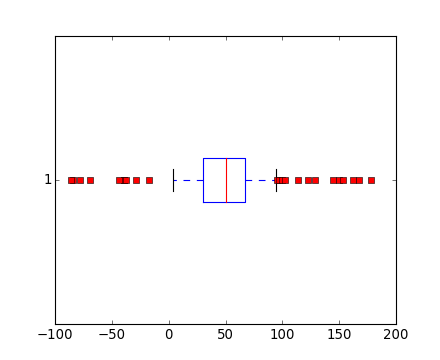
boxplot(data, 0, 'rs', 0, 0.75)
# fake up some more data
spread = rand(50) * 100
center = ones(25) * 40
flier_high = rand(10) * 100 + 100
flier_low = rand(10) * -100
d2 = concatenate((spread, center, flier_high, flier_low), 0)
data.shape = (-1, 1)
d2.shape = (-1, 1)
#data = concatenate( (data, d2), 1 )
# Making a 2-D array only works if all the columns are the
# same length. If they are not, then use a list instead.
# This is actually more efficient because boxplot converts
# a 2-D array into a list of vectors internally anyway.
data = [data, d2, d2[::2, 0]]
# multiple box plots on one figure
figure()
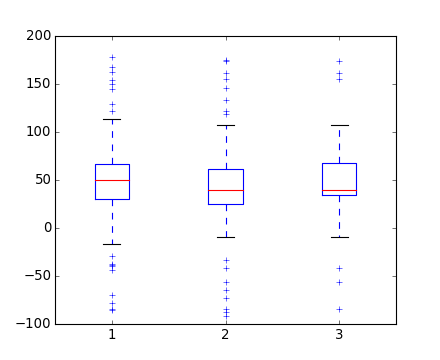
boxplot(data)
show()
Keywords: python, matplotlib, pylab, example, codex (see Search examples)